Benefits of load balancing Citrix StoreFront
The three top benefits of load balancing Citrix StoreFront are High Availability, optimal performance, and scalability:
- High Availability (HA): Load balancing ensures the continuous availability of the StoreFront service. By distributing traffic across multiple StoreFront servers, the failure of a single server doesn’t bring the entire service down. If one StoreFront server fails (goes offline, crashes, or is unresponsive), the load balancer automatically detects the failure and redirects all user traffic to the remaining healthy servers. This process, known as failover, is typically seamless to the end-user, meaning they can still access their virtual applications and desktops without interruption or significant delay. This is crucial for maintaining business continuity.
- Optimal performance: Load balancing prevents any single StoreFront server from becoming a bottleneck, ensuring a faster and more consistent login and application launch experience for users. Requests are intelligently distributed across all active servers. This prevents overload on any one server, leading to better response times, especially during peak usage. By spreading the processing load, the time it takes for a user to authenticate and load their available resources is minimized, resulting in a more responsive and positive user experience.
- Scalability: Load balancing makes it easy to grow and maintain the StoreFront environment without causing downtime. Organizations can easily add more StoreFront servers to the load-balanced group as the number of users or the workload increases. The load balancer automatically incorporates the new servers and starts directing traffic to them, making the environment highly scalable. Administrators can also isolate (take out of service) a single StoreFront server from the load balancer, perform maintenance (like patching, upgrades, or configuration changes) on it, and then bring it back online. They can then repeat this process for the other servers, achieving rolling updates and zero-downtime maintenance.
About Citrix StoreFront
Citrix StoreFront is an enterprise app store for users that aggregates and presents virtual app and desktop resources from on-premises and hybrid deployments.
Citrix StoreFront is an enterprise-grade application which provides users with easy, point and click access to full virtualized desktops as well as specific virtualized applications. StoreFront makes it simple to provide access to virtualized infrastructure both via its web interface as well as the cloud-based Citrix Workspace desktop application.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Citrix StoreFront?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Citrix StoreFront
The load balancer can be deployed in 4 fundamental ways: Layer 4 DR mode, Layer 4 NAT mode, Layer 4 SNAT mode, and Layer 7 Reverse Proxy (Layer 7 SNAT mode).
For Citrix StoreFront, using Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is recommended.
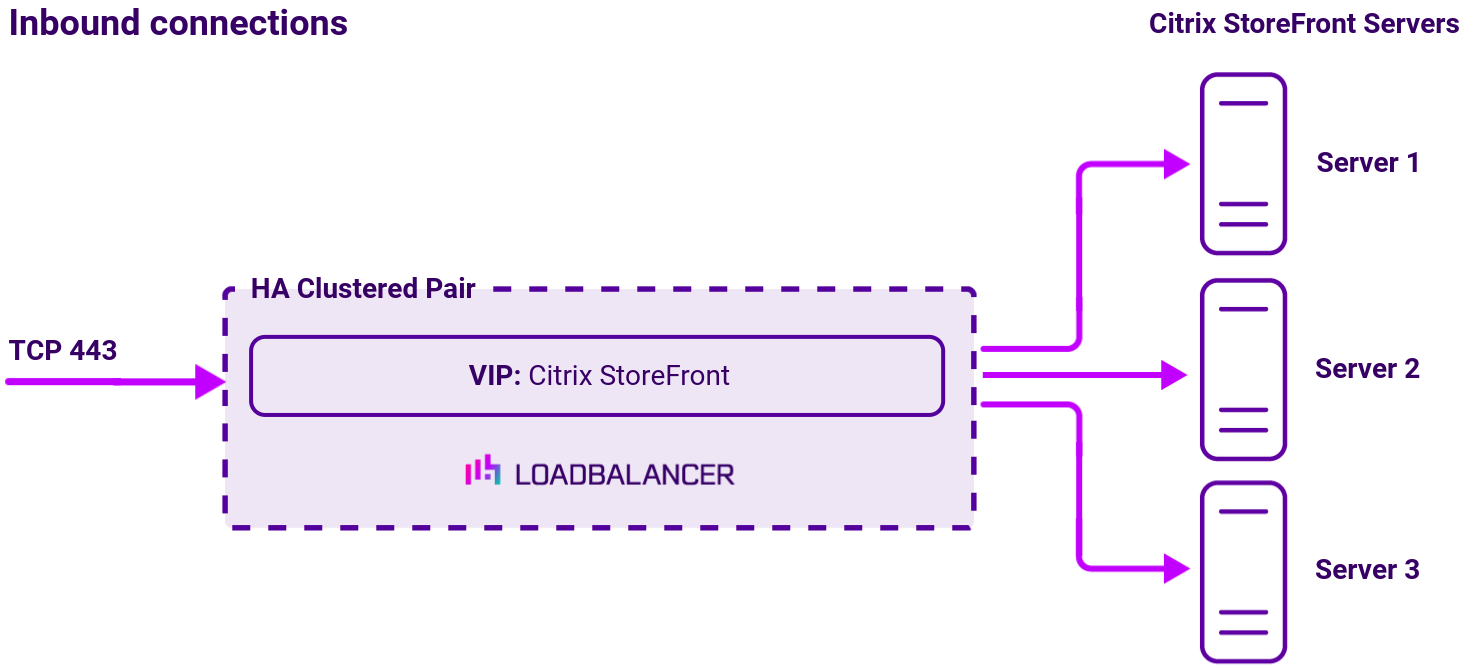
Virtual service (VIP) requirements
To provide load balancing and HA for Citrix StoreFront, a single VIP is required:
- Citrix StoreFront (HTTPS)
Load balancing deployment concept
Note
The load balancer can be deployed as a single unit, although Loadbalancer.org recommends a clustered pair for resilience & high availability.
Load balancing topology
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy can be deployed using either a one-arm or two-arm configuration. For two-arm deployments, eth1 is typically used for client side connections and eth0 is used for Real Server connections, although this is not mandatory since any interface can be used for any purpose.
For more on one and two-arm topology see Topologies & Load Balancing Methods.
About Layer 7 Reverse Proxy load balancing
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy uses a proxy (HAProxy) at the application layer. Inbound requests are terminated on the load balancer and HAProxy generates a new corresponding request to the chosen Real Server. As a result, Layer 7 is typically not as fast as the Layer 4 methods. Layer 7 is typically chosen when either enhanced options such as SSL termination, cookie based persistence, URL rewriting, header insertion/deletion etc. are required, or when the network topology prohibits the use of the Layer 4 methods.
The image below shows an example Layer 7 Reverse Proxy network diagram:
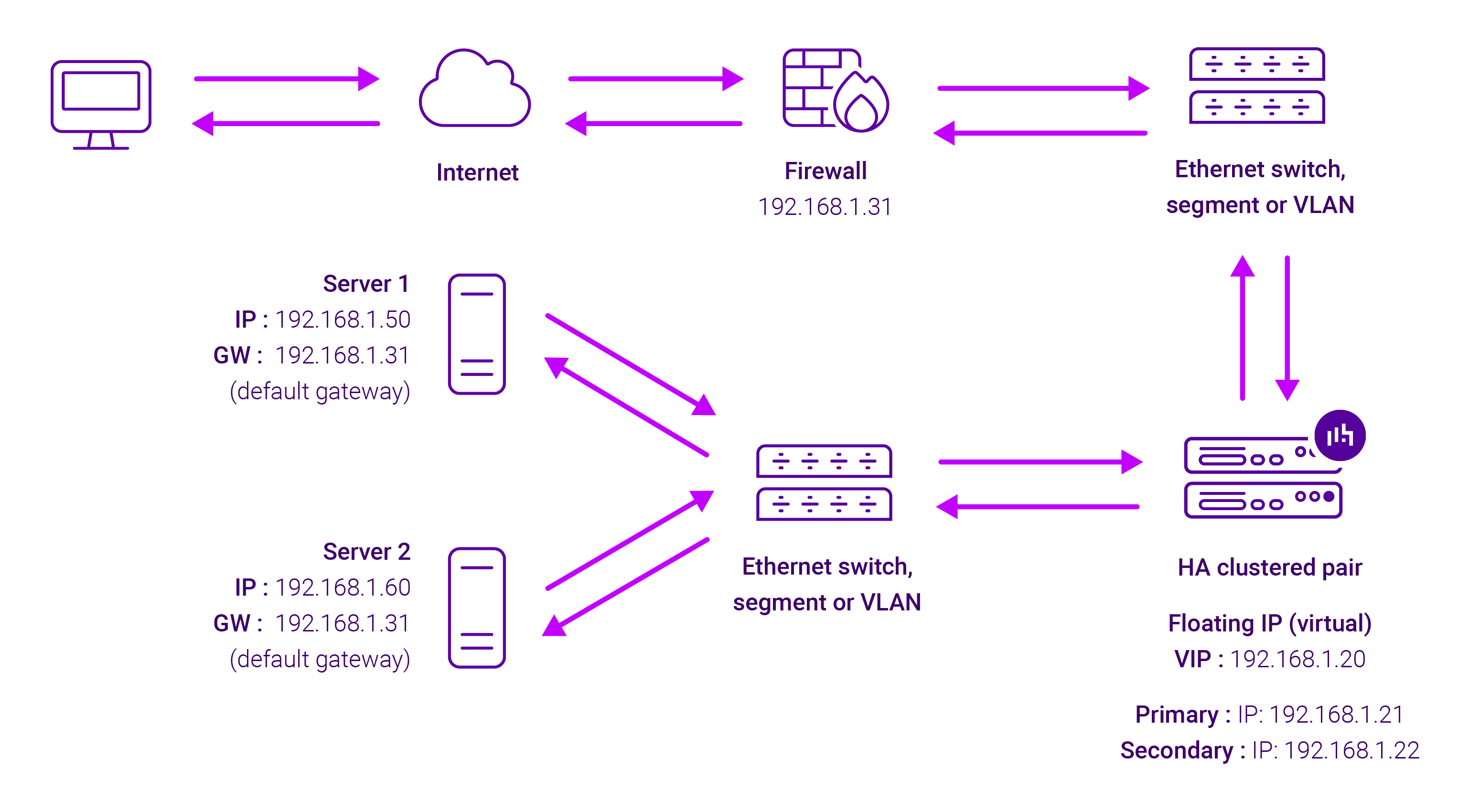
Because Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is a full proxy, Real Servers in the cluster can be on any accessible network including across the Internet or WAN.
Layer 7 Reverse Proxy is not transparent by default, i.e. the Real Servers will not see the source IP address of the client, they will see the load balancer’s own IP address by default, or any other local appliance IP address if preferred (e.g. the VIP address).
This can be configured per Layer 7 VIP. If required, the load balancer can be configured to provide the actual client IP address to the Real Servers in 2 ways. Either by inserting a header that contains the client’s source IP address, or by modifying the Source Address field of the IP packets and replacing the IP address of the load balancer with the IP address of the client. For more information on these methods, please refer to Transparency at Layer 7 in the Enterprise Admin Manual.